Case Study: Galvanising Plants
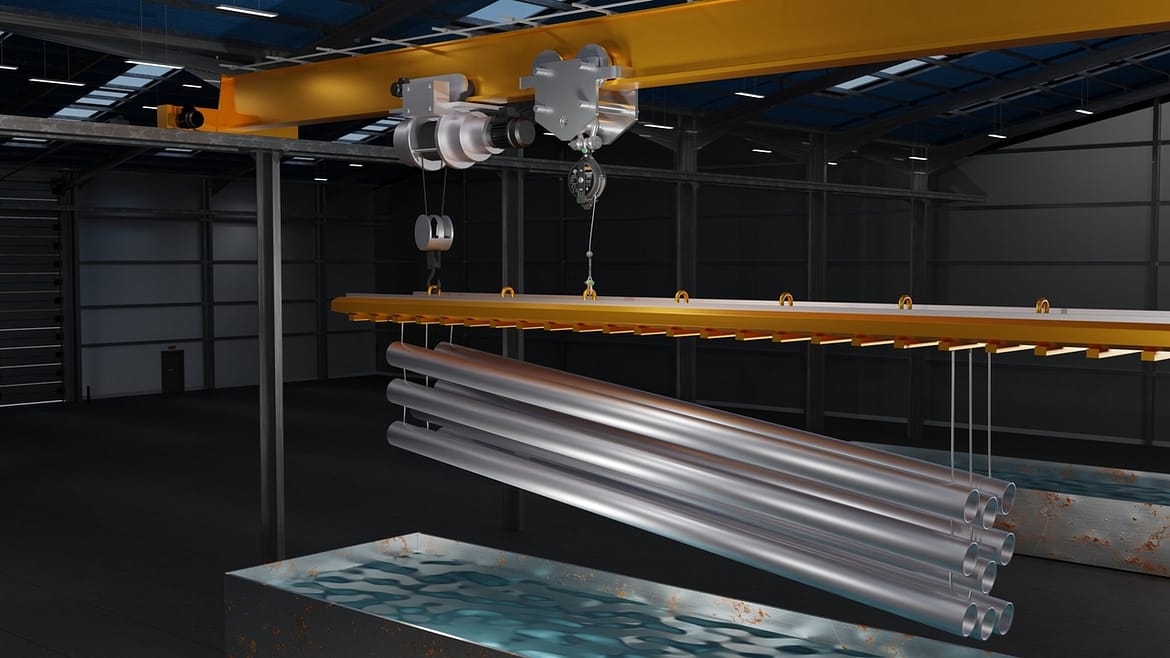
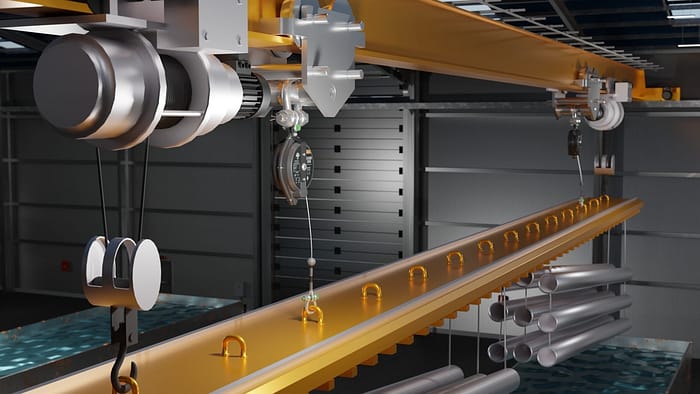
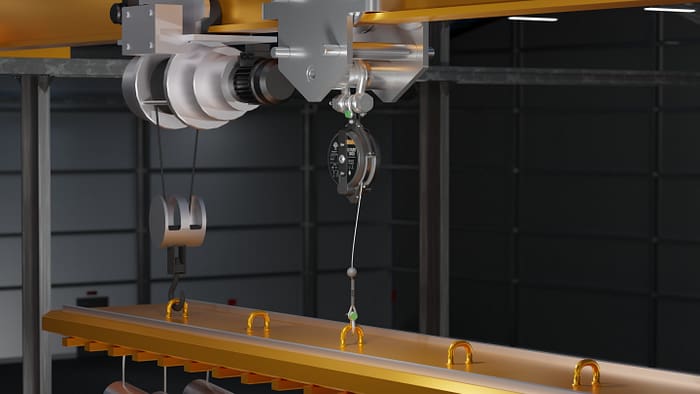
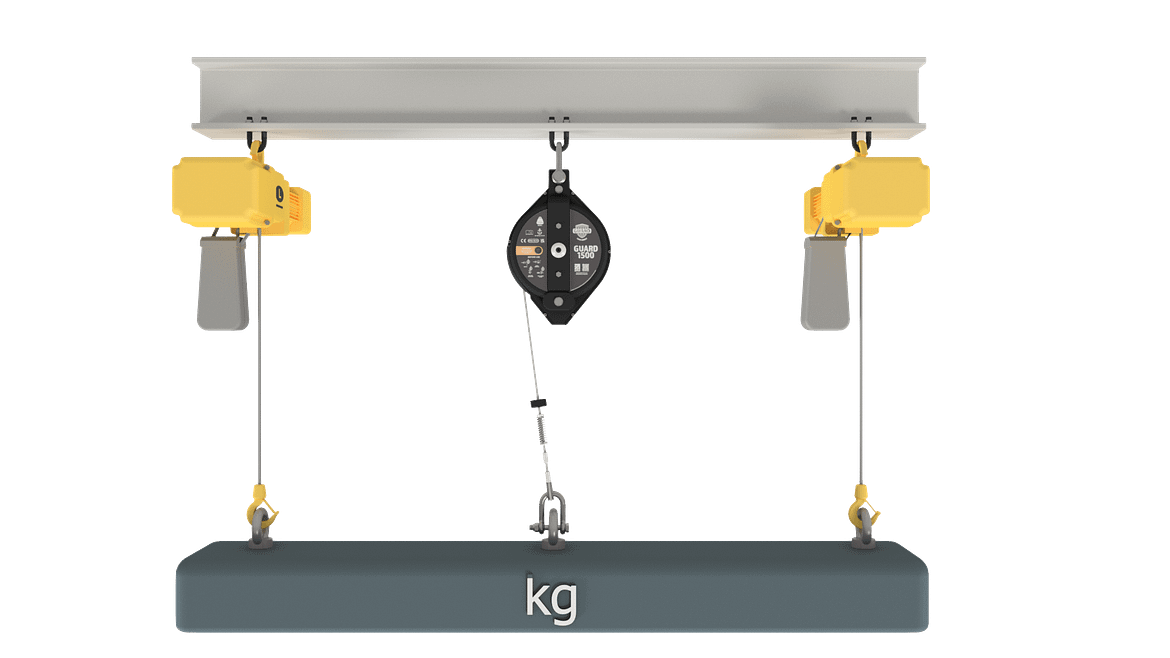
Using a load arrestor in a galvanising plant can enhance safety by preventing accidents and injuries related to the handling of heavy loads, such as metal objects, being moved during the galvanizing process. A load arrestor, also known as a 'Guard', 'load arrest device' or 'load arrester', is a device designed to limit the movement of a load in the event of a failure in the lifting equipment, normally a hoist. Here's how load arrestors can be beneficial in a galvanising plant:
- Preventing Accidents: Load arrestors provide an additional layer of safety by restricting uncontrolled movements of heavy loads. In the galvanizing process, large metal objects are lifted and moved, which can pose a significant risk if the lifting equipment fails. A load arrestor can prevent these loads from falling and causing accidents.
- Emergency Stop: Load arrestors are equipped with an emergency stop mechanism that quickly stops the movement of a load in case of an accidental fall, such as when the lifting equipment malfunctions. This can prevent further accidents and injuries.
- Reduction of Impact Forces: Load arrestors are designed to absorb and dissipate energy, reducing the impact forces that would otherwise occur is the emergency brake engages. This is particularly important in preventing damage to both the load and the surrounding equipment.
- Worker Safety: Load arrestors can improve the safety of workers involved in the lifting and movement of heavy loads. By providing a controlled arrest of the load's movement, the risk of sudden load drops or swings is minimized.
When implementing load arrestors in a galvanizing plant, consider the following:
- Proper Installation: Load arrestors should be installed according to the manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations.
- Regular Maintenance: Like all safety equipment, load arrestors need regular inspections and maintenance to ensure they are in proper working condition. This is especially important in galv. plants, where vapours create a more corrosive environment.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the load arrestors are compatible with the specific loads used in your galvanizing plant.
- Compliance: Check if there are any relevant industry standards or regulations that specify the use of load arrestors in galvanizing plants. Compliance with these standards is important for ensuring the highest level of safety.
Before installing load arrestors, it's advisable to consult with safety experts, equipment manufacturers, and industry guidelines to determine the most suitable type of load arresters for your plant's needs and to ensure proper integration into your safety protocols. Be sure to contact Guard Load Arrest if you require advice about your particular setup.
Protecting Equipment that is Suspended at Height
If you're looking for information about how to protect equipment that is suspended at height, you're in the right place!
Protecting equipment that is suspended at height is an important aspect of workplace safety, especially in industries such as construction, maintenance, and industrial operations where workers often interact with elevated equipment. Proper equipment protection helps prevent damage, accidents, and potential injuries. Here are some key considerations and strategies for protecting suspended equipment:
- Anchorage and Rigging Points: Ensure that the anchorage points, rigging, and support structures used to suspend the equipment are robust, well-maintained, and properly rated for the intended load. Regular inspections and load calculations are essential to ensure the stability and safety of the equipment.
- Fall Protection: If workers need to access or work around suspended equipment, they should be equipped with appropriate fall protection gear. This includes harnesses, lanyards, and self-retracting lifelines. Fall arrest systems help prevent workers from falling in case of a slip or mishap.
- Load Arrest: If there is any risk that suspended equipment would fall, installing a load arrest device(s) should be considered. Specifically designed to be used in collaboration with primary lifting devices, such as hoists, load arrestors provide a crucial secondary safety back-up for overhead loads. Should the primary device or support fail, Guard load arrestors automatically stop the load from falling, thereby preventing damage to the load and, most importantly, protecting people or assets below.
- Protective Covers: Depending on the nature of the equipment, consider using protective covers or enclosures to shield it from environmental elements like rain, dust, and UV radiation. This helps prolong the life of the equipment and maintain its functionality.
- Anti-Swing Measures: Suspended equipment can sway or swing due to wind or movement, which can pose risks to both equipment and workers. Implement anti-swing devices or techniques to minimize swinging and ensure stability. This might include using dampening systems or controlling movement through tag lines.
- Lockout/Tagout: If the suspended equipment is part of a system that requires maintenance or repair, follow proper lockout/tagout procedures. Lockout/tagout involves isolating and securing energy sources to prevent accidental startup while maintenance is being performed.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Establish a routine inspection and maintenance schedule for both the suspended equipment and the rigging systems. Any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage should be promptly addressed. Proper maintenance helps prevent unexpected failures and ensures safe operation.
- Training: Workers who interact with suspended equipment should receive proper training on its safe use, as well as emergency procedures in case of accidents or malfunctions. Training promotes awareness and helps workers respond effectively to potential hazards.
- Emergency Preparedness: Have clear emergency protocols in place in case of equipment failure, accidents, or unexpected incidents. Workers should know how to respond to emergencies and how to evacuate the area safely.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of inspections, maintenance activities, and any modifications made to the suspended equipment or rigging systems. Documentation helps track the equipment's history and ensures that it's kept in safe working condition.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure that all safety measures are in compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations. Adhering to safety guidelines helps minimize risks and potential liabilities.
Remember that protecting suspended equipment is a comprehensive effort that involves multiple factors. Prioritize safety, regular maintenance, and adherence to best practices to create a secure working environment for both equipment and workers.